A sustainable solution
While the buildings and construction sector accounts for 30% of global energy use and 27%
of emissions, Hygieia is seizing the moment to make positive change.
This can be achieved by minimising the emissions or resources required to deliver high-quality health
outcomes, for example, reducing waste associated with procedures, using more sustainable products /
materials and/or the reuse, repurpose, or recycling of our CDC modular buildings, providing a legacy use.
Reusing and recycling materials have long been key tenets of sustainability. Construction can apply these
green principles by opting to use salvaged materials in their projects. Doing so gives construction materials
a second life and helps keep waste out of landfills. An example of this for Hygieia is the use of high recycled content within the steel sections from Tata Steel.
The facilities should be designed with energy efficiency in mind. Through working with mechanical engineers,
architects and designers, facilities can design a high-performance building envelope that maintains
the indoor comfort over outdoor elements such as temperature, air, humidity, and noise while also
lowering the lifetime operating costs of a facility. Minimised energy consumption also helps to reduce
the renewable energy required on the site to achieve Net Zero Energy design.
We will be working with several supply chain partners where innovative sustainable products are available.
We have utilised plastic curbs produced from recycled water bottles, we have utilised sheep’s wool for building
insulation over conventional inert products, and we have considered alternative cladding / façade materials
recycled from white goods, IT equipment, and plastic toys. We have a host of vetted suppliers with products
that offer a high percentage level of recycled content and we will strive to utilise the best products available.
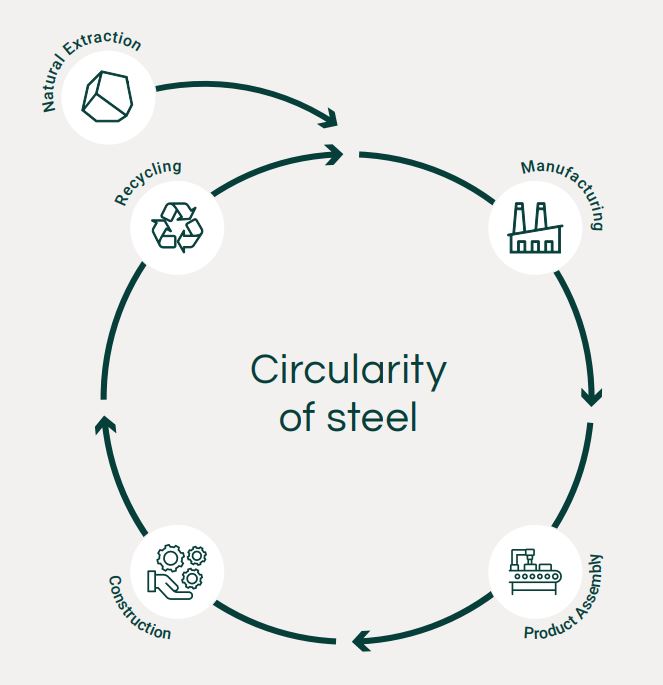
Recycling, reuse, and the circular economy
Some key trends that contribute to the growth of the Circular Economy include the increasing awareness of environmental issues, advanced recycling technologies, innovative product designs that focus on modularity and lifespan extension, the rise of sharing economy platforms, and policies and regulations supporting circularity.
Hygieia CDC buildings are designed to have a future legacy, through reuse, repurposing, or recycling. We believe that true innovation is not only about creating new products but also about improving existing ones and making them more sustainable. One way to achieve this is by applying the principles of the circular economy, with the aim of reducing waste, reusing resources, and regenerating natural systems.
Annual global resource consumption exceeded 100 billion tonnes in 2017, almost doubling the per capita consumption rate of 50 years ago, and jumping 8% in just 2 years. Of this figure, the construction industry is responsible for between one-third and 40% and a similarly high proportion of waste, as very few construction components and materials are reused or recycled. Indeed, some construction materials are never used before they are scrapped, research suggests that as much as 13% in the UK.
Material efficiency is at the heart of circular approaches in construction, as well as designing for adaptation,
and disassembly, and preserving the value of materials beyond their initial use. A key conceptual shift is to think of buildings not just for their primary purpose, but also as a method of storing thousands of tonnes of valuable products and materials, which can be traded and reused at the end of the building’s life, rather than just discarded.
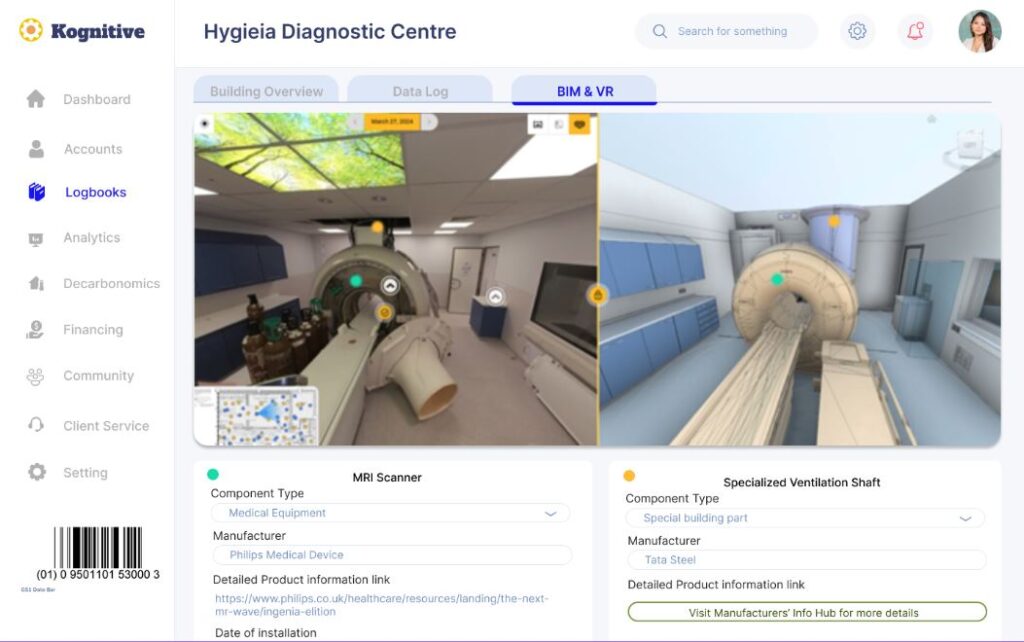
Hygieia will be one of the first companies to provide Digital Logbooks with the new CDC modular buildings.
A Digital Building Logbook is an all-in-one information tool meant to encourage data transparency and availability and simplify decision-making for stakeholders across the building’s value chain. The data logging of key recyclable components will allow a higher percentage of recyclability of, for example, steel components, should the modular building not be repurposed or reused.
In addition, we use components in the construction of our CDCs that can be reused across a range of sectors in other buildings for other uses.
Biophilic design
Biophilic design has been found to support cognitive function, physical health, and psychological well-being. Biophilia is defined as the innate human instinct to connect with nature and other living beings and comprises the 5 senses; sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing. The ultimate goal is to use these in conjunction with each other to create a space that re-energizes its occupants.
Biophilic design can be organised into three categories – Nature in the Space, Natural Analogues, and Nature of the Space – providing a framework for understanding and enabling thoughtful incorporation of a rich diversity of strategies into the built environment. It aims to use sustainable materials by default as we encourage the use of wood grain, plants to reduce VOCs, airflow through windows, better acoustics, natural lighting, and many more innovative solutions.